Written by: PATRICIA RYAN
Quick Guide: Endocannabinoid System (ECS)
ECS, discovered as recently as 1992, is recognized as one of the most important modulatory systems of the human body today. The ultimate function of the ECS is to maintain a stable internal environment despite changes in the external environment. This stability is known as homeostasis, which endocannabinoids promote at the most basic levels.
Some key functions of the ECS in promoting homeostasis are protecting, relaxing, eating, forgetting, and sleeping.
Preclinical data from these two studies show that the ECS has a profound effect on stress, anxiety, and depressive states at the pharmacologic, biochemical, and genetic levels.
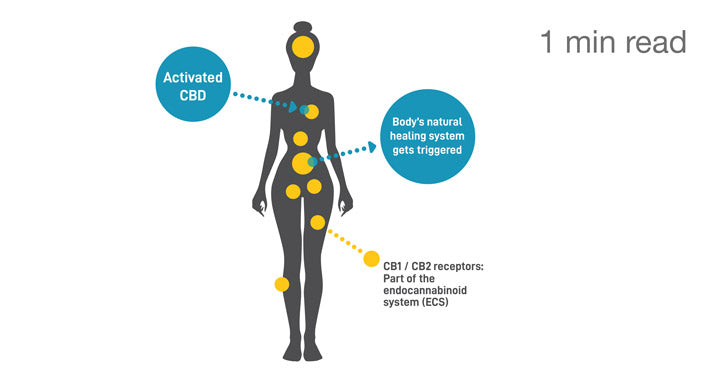
Humans (and all mammals) naturally produce endocannabinoids which are molecules that interact with a specific neurological network – much like the way that endorphins, serotonin, and dopamine do in our bodies.
They help regulate “memory, balance, movement, immune health, and neuroprotection” among many other basic functions according to Dr. Raphael Mechoulam, the pioneering scientist who made many ground breaking discoveries in this field. Some of the most common receptors in our bodies, CB1 and CB2 receptors, process these endocannabinoids. “Exercise, for example, has shown to elevate endocannabinoid levels in the brain. This probably accounts for what jogging enthusiasts call runner’s high” says Dr. Mechoulam.
Interestingly, cannabinoids such as CBD, THC, CBN, CBG derived from both hemp and cannabis plants have almost identical molecular structure to endocannabinoids that our bodies create. These plant-derived molecules interact the same way as endocannabinoids interact with CB1 and CB2 receptors in the body.
These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. These products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease.



Share Your Thoughts
We won't share, sell or publish your email address.